
|
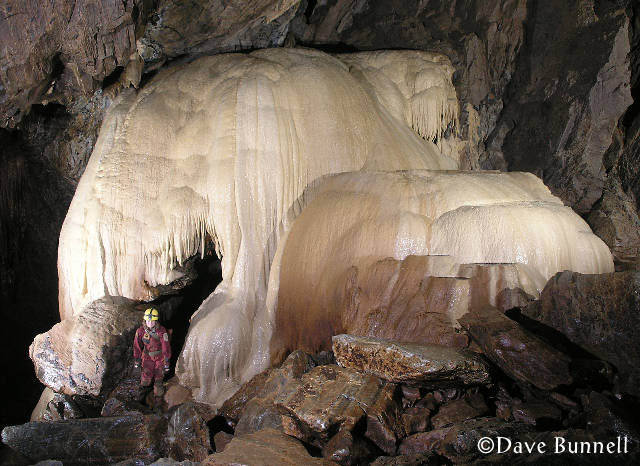
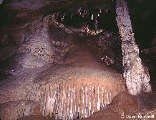
Flowstone is perhaps the most common
of all cave deposits, and is almost always composed of calcite or other
carbonate minerals. It forms in thin layers which initially take on
the shape of the underlying floor or wall bedrock beneath, but tends
to become rounded as it gets thicker. Flowstone masses are often fluted
with draperies at their lower
end, such as the area above the caver's head. Impurities in the calcite
may give a variety of colors to flowstone, such
as the reddish areas on the right (likely due to iron).
Flowstone forms from actively flowing water (rather than water squeezed through cracks) in which carbon dioxide is lost and carbonate material is deposited. This is the basic mechanism forming stalagmites as well, and the two often form together. Continuous flowstone deposits may cover vast areas of a cave floor or flow for hundreds of vertical feet down the side of vertical shafts. |
![]()

 |
 |
 |
 |
Click on a thumbnail to view more flowstone images.
![]()
| Back to: | |
 |
Created: December, 1998 |